You Uploaded an Apk or Android App Bundle Signed With a Certificate That Expires Too Soon
Android requires that all APKs be digitally signed with a certificate earlier they are installed on a device or updated. When releasing using Android App Bundles, you need to sign your app bundle with an upload key before uploading it to the Play Console, and Play App Signing takes care of the rest. For apps distributing using APKs on the Play Store (created earlier August 2021) or on other stores, you must manually sign your APKs for upload.
This page guides you lot through some important concepts related to app signing and security, how to sign your app for release to Google Play using Android Studio, and how to configure Play App Signing.
The following is a high-level overview of the steps yous might need to accept to sign and publish a new app to Google Play:
- Generate an upload fundamental and keystore
- Sign your app with your upload key
- Configure Play App Signing
- Upload your app to Google Play
- Prepare & curl out release of your app
If instead your app is already published to the Google Play Store with an existing app signing key, or you would similar to cull the app signing fundamental for a new app instead of having Google generate it, follow these steps:
- Sign your app with your app's signing key and select the choice to encrypt and export its signing key.
- Upload your app's signing cardinal to Play App Signing.
- (Recommended) Generate and register an upload document for future updates to your app
- Upload your app to Google Play
- Set up & roll out release of your app
This page also explores how to manage your own keys for when uploading your app to other app stores. If you practise non use Android Studio or would rather sign your app from the control line, larn about how to use apksigner.
Play App Signing
With Play App Signing, Google manages and protects your app'southward signing key for you and uses information technology to sign your APKs for distribution. And, considering app bundles defer building and signing APKs to the Google Play Store, yous need to configure Play App Signing before you upload your app parcel. Doing so lets you benefit from the post-obit:
- Use the Android App Bundle and back up Google Play'due south avant-garde delivery modes. The Android App Bundle makes your app much smaller, your releases simpler, and makes it possible to use feature modules and offer instant experiences.
- Increment the security of your signing key, and make it possible to use a split upload key to sign the app bundle you upload to Google Play.
-
One time key upgrade for new installs lets you change your app signing key in case your existing one is compromised or if you need to drift to a cryptographically stronger key
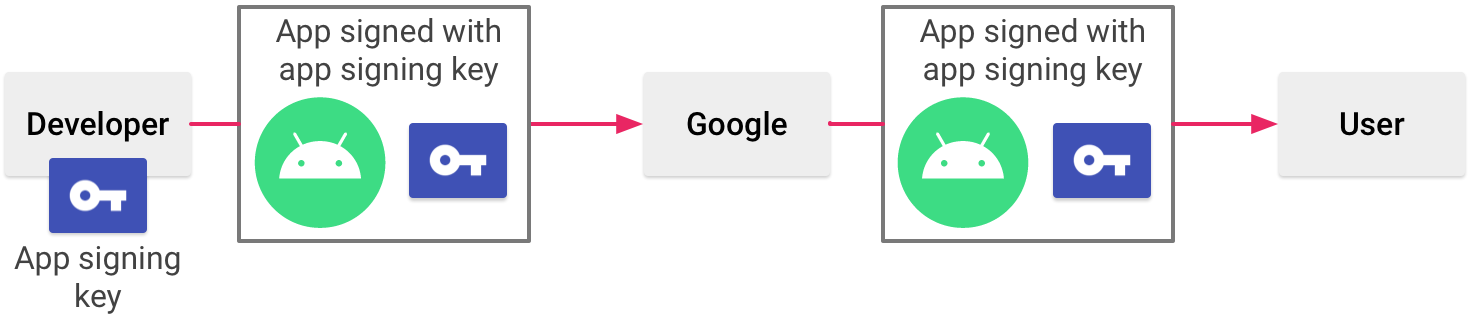
Play App Signing uses two keys: the app signing central and the upload cardinal, which are described in further particular in the section virtually Keys and keystores. You keep the upload primal and utilize it to sign your app for upload to the Google Play Store. Google uses the upload certificate to verify your identity, and signs your APK(s) with your app signing key for distribution every bit shown in figure 1. By using a split upload key yous can request an upload fundamental reset if your fundamental is ever lost or compromised.
By comparing, for apps created before Baronial 2021 that have not opted in to Play App Signing, if you lose your app'south signing central, you lose the ability to update your app.
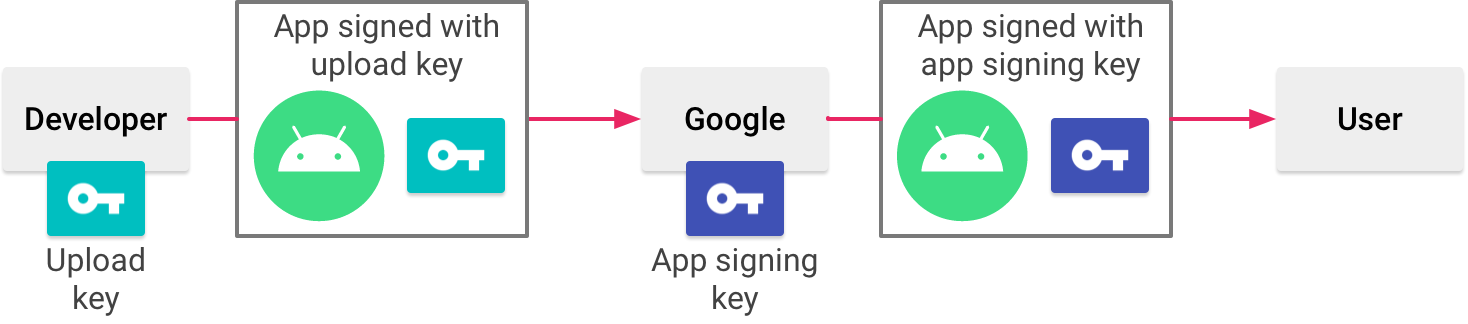
Figure ane. Signing an app with Play App Signing
Your keys are stored on the same infrastructure that Google uses to store its own keys, where they are protected past Google's Key Direction Service. You can learn more than about Google'due south technical infrastructure by reading the Google Cloud Security Whitepapers.
When you apply Play App Signing, if you lose your upload key, or if it is compromised, you lot can contact Google to revoke your old upload cardinal and generate a new one. Considering your app signing cardinal is secured by Google, y'all can keep to upload new versions of your app equally updates to the original app, even if you change upload keys. To learn more, read Reset a lost or compromised private upload key.
The side by side section describes some important terms and concepts related to app signing and security. If you'd rather skip alee and learn how to prepare your app for upload to the Google Play Store, become to Sign your app for release.
Keystores, keys, and certificates
Java Keystores (.jks or .keystore) are binary files that serve as repositories of certificates and individual keys.
A public key certificate (.der or .pem files), also known as a digital certificate or an identity certificate, contains the public primal of a public/individual cardinal pair, equally well equally some other metadata identifying the possessor (for case, name and location) who holds the corresponding private key.
The following are the different types of keys yous should understand:
- App signing primal: The cardinal that is used to sign APKs that are installed on a user'due south device. As function of Android'south secure update model, the signing key never changes during the lifetime of your app. The app signing key is private and must be kept secret. Y'all tin can, however, share the certificate that is generated using your app signing primal.
-
Upload key: The central y'all use to sign the app bundle or APK before you upload it for app signing with Google Play. You must keep the upload central hush-hush. However, you can share the document that is generated using your upload fundamental. You may generate an upload key in one of the following ways:
- If you lot choose for Google to generate the app signing key for you lot when you lot opt in, then the fundamental you employ to sign your app for release is designated as your upload cardinal.
- If you provide the app signing primal to Google when opting in your new or existing app, and then you have the option to generate a new upload fundamental during or after opting in for increased security.
- If you lot do not generate a new upload fundamental, you go along to utilise your app signing fundamental equally your upload key to sign each release.
Tip: To go along your keys secure, it's a proficient idea to make sure your app signing key and upload key are different.
Working with API providers
You lot can download the certificate for the app signing key and your upload key from the Release > Setup > App Integrity folio in the Play Console. This is used to register public fundamental(s) with API providers; information technology's intended to be shared, every bit it does not contain your private key.
A document fingerprint is a short and unique representation of a certificate that is often requested by API providers alongside the package proper name to register an app to use their service. The MD5, SHA-1 and SHA-256 fingerprints of the upload and app signing certificates tin be found on the app signing page of the Play Console. Other fingerprints tin likewise exist computed by downloading the original certificate (.der) from the same page.
Sign your debug build
When running or debugging your project from the IDE, Android Studio automatically signs your app with a debug certificate generated by the Android SDK tools. The first time yous run or debug your project in Android Studio, the IDE automatically creates the debug keystore and certificate in $Home/.android/debug.keystore, and sets the keystore and fundamental passwords.
Considering the debug certificate is created past the build tools and is insecure past design, most app stores (including the Google Play Store) exercise non accept apps signed with a debug certificate for publishing.
Android Studio automatically stores your debug signing information in a signing configuration then you exercise non have to enter it every time you lot debug. A signing configuration is an object consisting of all of the necessary information to sign your app, including the keystore location, keystore password, key name, and key password.
For more information about how to build and run apps for debugging, run into Build and Run Your App.
Expiry of the debug certificate
The cocky-signed certificate used to sign your app for debugging has an expiration date of xxx years from its creation date. When the certificate expires, you lot get a build fault.
To set this problem, simply delete the debug.keystore file stored in one of the post-obit locations:
-
~/.android/on Os X and Linux -
C:\Documents and Settings\user\.android\on Windows XP -
C:\Users\user\.android\on Windows Vista and Windows 7, 8, and 10
The next time y'all build and run a debug version of your app, Android Studio regenerates a new keystore and debug fundamental.
Sign your app for release to Google Play
When you are set to publish your app, you lot demand to sign your app and upload it to an app store, such as Google Play. When publishing your app to Google Play for the offset time, you must too configure Play App Signing. Play App Signing is optional for apps created earlier Baronial 2021. This section shows you lot how to properly sign your app for release and configure Play App Signing.
Generate an upload central and keystore
If y'all don't already have an upload key, which is useful when configuring Play App Signing, you tin can generate one using Android Studio equally follows:
- In the menu bar, click Build > Generate Signed Bundle/APK.
- In the Generate Signed Bundle or APK dialog, select Android App Package or APK and click Next.
- Below the field for Key store path, click Create new.
-
On the New Cardinal Shop window, provide the following data for your keystore and fundamental, equally shown in figure 2.
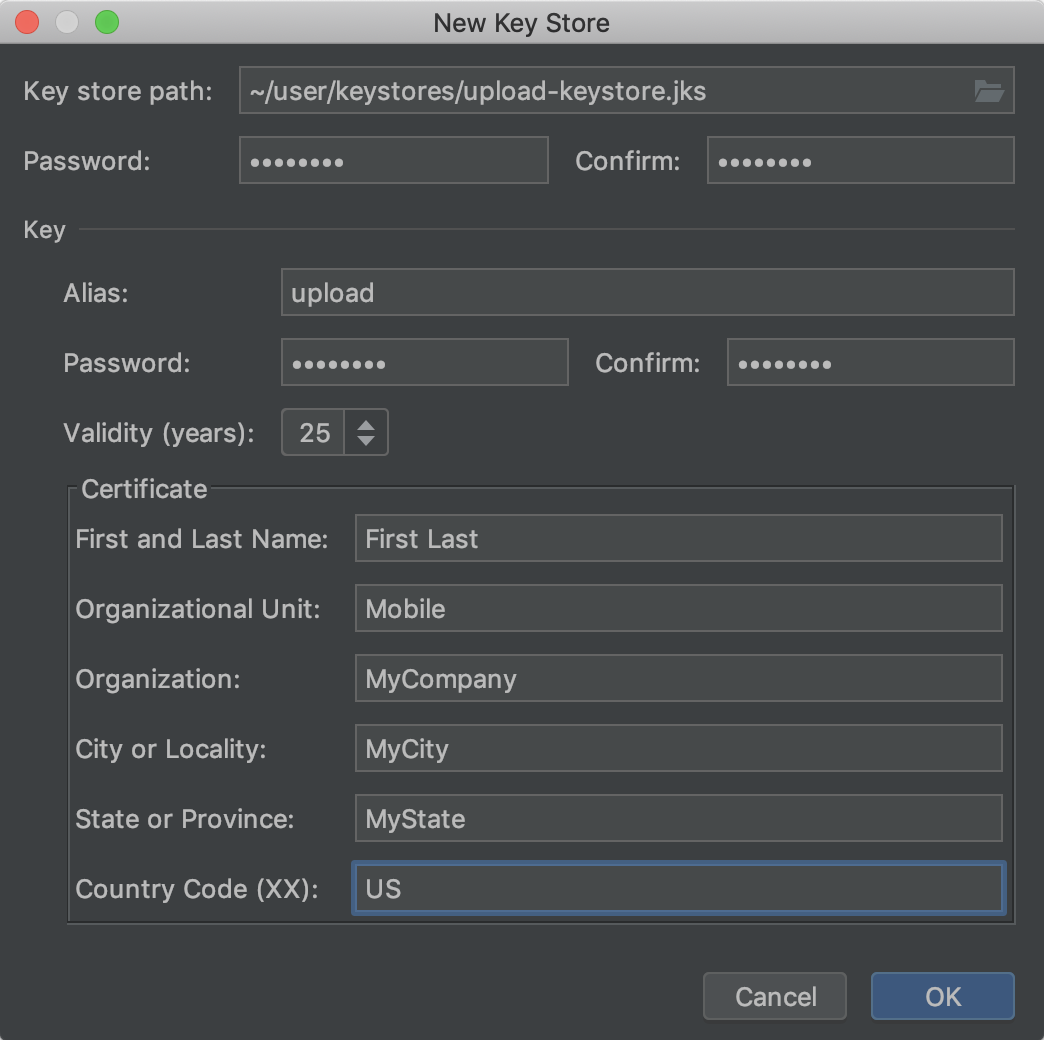
Figure 2. Create a new upload key and keystore in Android Studio.
-
Keystore
- Key shop path: Select the location where your keystore should exist created. Also, a file name should be added to the end of the location path with the
.jksextension. - Password: Create and confirm a secure countersign for your keystore.
- Key shop path: Select the location where your keystore should exist created. Also, a file name should be added to the end of the location path with the
-
Central
- Alias: Enter an identifying name for your central.
- Password: Create and confirm a secure password for your key. This should exist the same every bit your keystore countersign. (Delight refer to the known upshot for more information)
- Validity (years): Ready the length of time in years that your key will be valid. Your key should exist valid for at least 25 years, so you can sign app updates with the aforementioned key through the lifespan of your app.
- Certificate: Enter some information about yourself for your certificate. This information is non displayed in your app, but is included in your certificate as part of the APK.
-
Once yous complete the form, click OK.
-
If you lot would similar to build and sign your app with your upload key, keep to the department nearly how to Sign your app with your upload key. If you lot merely want to generate the key and keystore, click Cancel.
Sign your app with your key
If you lot already have an upload key, use it to sign your app. If instead your app is already signed and published to the Google Play store with an existing app signing central, use it to sign your app and make sure to encrypt and export it to opt your app in to Play App Signing. Yous can afterwards generate a dissever upload primal and annals your upload key's public certificate with Google Play to sign and upload subsequent updates to your app.
To sign your app using Android Studio, and export an existing app signing key, follow these steps:
- If you don't currently have the Generate Signed Bundle or APK dialog open, click Build > Generate Signed Bundle/APK.
- In the Generate Signed Bundle or APK dialog, select either Android App Bundle or APK and click Next.
- Select a module from the drop down.
-
Specify the path to your keystore, the alias for your key, and enter the passwords for both. If y'all haven't yet prepared your upload keystore and fundamental, commencement Generate an upload central and keystore and and so return to complete this step.
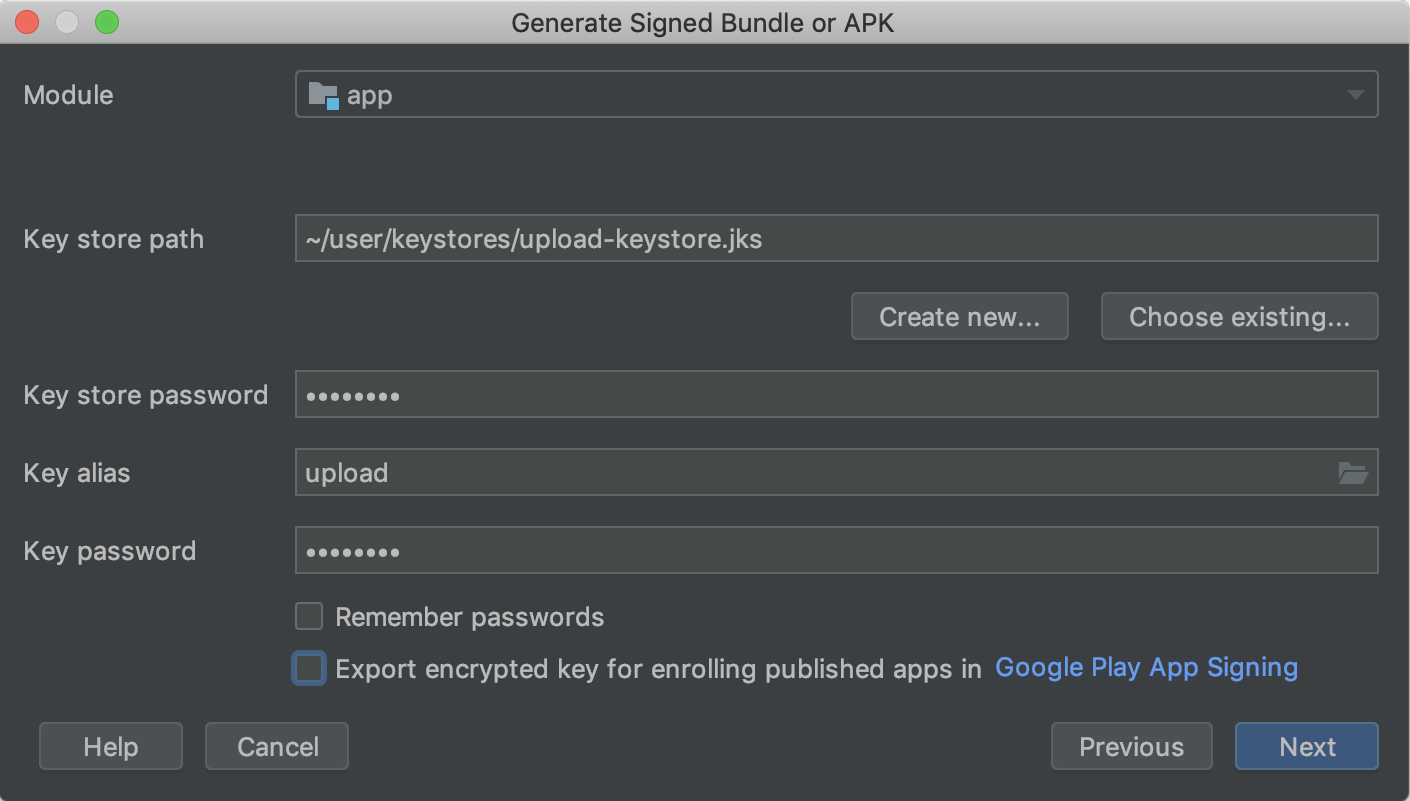
Figure three. Sign your app with your upload key.
-
If y'all're signing an app packet with an existing app signing central, and you lot'd like to later opt your app in to Play App Signing, cheque the box adjacent to Export encrypted primal and specify a path to save your signing key equally an encrypted
*.pepkfile. Yous can then use your encrypted app signing key to opt in an existing app into Play App Signing. -
Click Adjacent.
-
In the adjacent window (shown in figure 4), select a destination folder for your signed app, select the build type, choose the production flavor(s) if applicable.
-
If you are building and signing an APK, you need to select which Signature Versions y'all want your app to support. To learn more, read near app signing schemes
-
Click End.
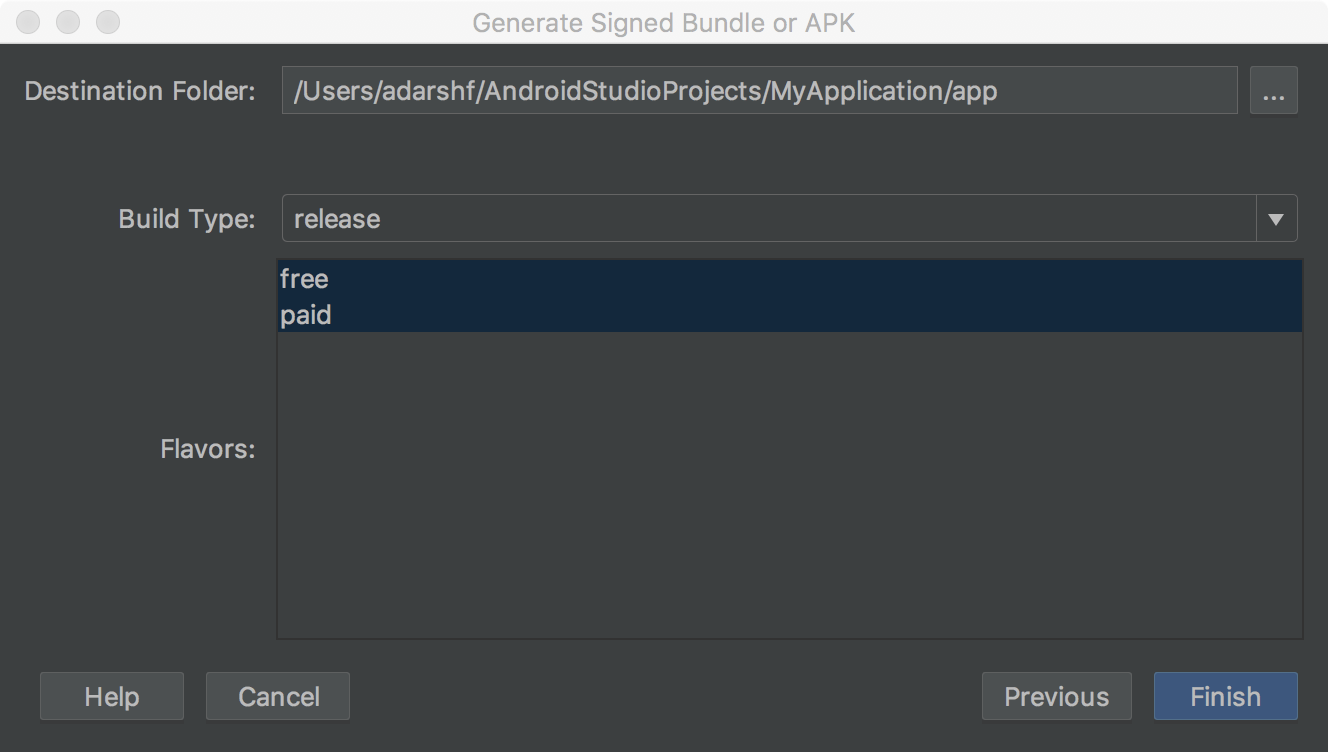
Figure iv. Generate a signed version of your app for the selected product flavors.

Figure 5. Click the link in the popup to analyze or locate your app package, or locate your exported signing key.
After Android Studio finishes edifice your signed app, you tin either locate or clarify your app by clicking on the appropriate option in the popular-upward notification. If you selected the option to export your signing key, yous tin can quickly navigate to information technology by clicking the dropdown arrow in the bottom right corner of the popup to expand information technology and clicking Show Exported Key File, equally shown in figure 5.
Now yous're ready to opt your app in to Play App Signing and upload your app for release. If you're new to the app publishing process, you may want to read the Launch overview. Otherwise, go along to the page about how to Upload your app to the Play Panel.
Using Play App Signing
Equally described earlier in this folio, configuring Play App Signing is required to sign your app for distribution through Google Play (except for apps created before Baronial 2021, which may continue distributing self-signed APKs). The steps yous demand to take depend on whether your app has not withal been published to Google Play, or your app is already signed and was published before August 2021 using an existing app signing primal.
Configure a new app
To configure signing for an app that has non withal been published to Google Play, proceed as follows:
- If you haven't already done so, generate an upload key and sign your app with that upload key.
- Sign in to your Play Console.
- Follow the steps to prepare & gyre out your release to create a new release.
- Subsequently you choose a release rails, configure app signing under the App Integrity department as follows:
- To accept Google Play generate an app signing key for you and utilise it to sign your app, yous don't have to do anything. The primal you lot use to sign your first release becomes your upload cardinal, and you should use it to sign time to come releases.
- To use the same key as some other app on your developer business relationship, select Change app signing cardinal > Employ my own key > Use the same key every bit another app in this account, select an app, and then click Keep.
- To provide your ain signing key for Google to use when signing your app, select Alter app signing cardinal > Use my ain key and select one of the options that lets you securely upload a private fundamental and its public certificate.
In the section called App Bundles, click Browse files to locate and upload the app you lot signed using your upload primal. For more than information about releasing your app, refer to prepare & roll out your release. When you lot release your app subsequently configuring Play App Signing, Google Play generates (unless you lot upload an existing cardinal) and manages your app'south signing key for you. Simply sign subsequent updates to your app using your app's upload central before uploading information technology to Google Play.
If y'all need to create a new upload key for you app, get to the section about how to Reset a lost or compromised private upload cardinal.
Opt in an existing app
If you're updating an app that's already published to Google Play using an existing app signing primal, y'all tin can opt in to Play App Signing every bit follows:
- If you haven't already done so, sign your app using Android Studio with your existing app signing cardinal and brand sure to check the box next to Consign encrypted key to save your signing key equally an encrypted
*.pepkfile. You'll demand this file in a afterward footstep. This can too be washed using the PEPK tool, which you can download from the Play Console. - Sign in to your Play Console and navigate to your app.
- On the left menu, click Release > Setup > App integrity.
- If applicable, review the Terms of Service and select Accept.
- Select one of the options that all-time describes the signing key you desire to upload to Google Play and follow the instructions that are shown. For example, if you used Android Studio to consign your app's signing central, as described on this folio, select Upload a cardinal exported from Android Studio and upload the
*.pepkfile for your cardinal. - Click Enroll.
Y'all should now see a folio with the details of your app'south signing and upload certificates. Google Play now signs your app with your existing key when deploying it to users. However, ane of the most of import benefits to Play App Signing is the ability to split the fundamental yous use to sign the artifact you upload to Google Play from the primal that Google Play uses to sign your app for distribution to users. So, consider following the steps in the next department to generate and register a dissever upload central.
Generate and register an upload certificate
When y'all're publishing an app that is not signed past an upload key, the Google Play Console provides the option to register one for future updates to the app. Although this is an optional stride, it's recommended that you publish your app with a key that's split up from the i Google Play uses to distribute your app to users. That way, Google keeps your signing key secure, and you lot take the pick to reset a lost or compromised private upload key. This section describes how to create an upload fundamental, generate an upload certificate from it, and register that certificate with Google Play for future updates of your app.
The following describes the situations in which you encounter the option to register an upload document in the Play Console:
- When yous publish a new app that'due south signed with a signing key and opt information technology in to Play App Signing.
- When you are about to publish an existing app that's already opted in to Play App Signing, but it is signed using its signing cardinal.
If y'all are not publishing an update to an existing app that's already opted in to Play App Signing, and y'all'd like to register an upload certificate, consummate the steps below and go along on to the section about how to reset a lost or compromised individual upload key.
If you oasis't already done so, generate an upload fundamental and keystore.
After you create your upload key and keystore, you need to generate a public document from your upload key using keytool, with the post-obit command:
$ keytool -export -rfc -keystore your-upload-keystore.jks -alias upload-alias -file output_upload_certificate.pem
Now that yous accept your upload certificate, register it with Google when prompted in the Play Console or read the section below to annals it though the Google Play support team.
Upgrade your app signing key
In some circumstances, you might desire to alter your app's signing key. For example, because yous want a cryptographically stronger key or your signing cardinal has been compromised. However, considering users tin can merely update your app if the update is signed with the same signing fundamental, it'south hard to alter the signing key for an app that's already published.
If you publish your app to Google Play, you can upgrade the signing key for your published app through the Play Console—your new cardinal is used to sign new installs and app updates, while your older app signing cardinal is used to sign updates for users who installed your app before the key upgrade.
To learn more, read Upgrade your app signing key for new installs.
Reset a lost or compromised individual upload fundamental
If y'all lost your private upload key or your private key has been compromised, yous can create a new ane and contact the Google Play back up team to reset the fundamental.
Configure the build process to automatically sign your app
In Android Studio, y'all tin configure your project to sign the release version of your app automatically during the build process past creating a signing configuration and assigning it to your release build type. A signing configuration consists of a keystore location, keystore password, key alias, and primal password. To create a signing configuration and assign it to your release build type using Android Studio, complete the post-obit steps:
- In the Project window, right click on your app and click Open Module Settings.
- On the Project Structure window, under Modules in the left panel, click the module you lot would like to sign.
- Click the Signing tab, then click Add
 .
. -
Select your keystore file, enter a proper noun for this signing configuration (every bit you may create more than than ane), and enter the required information.
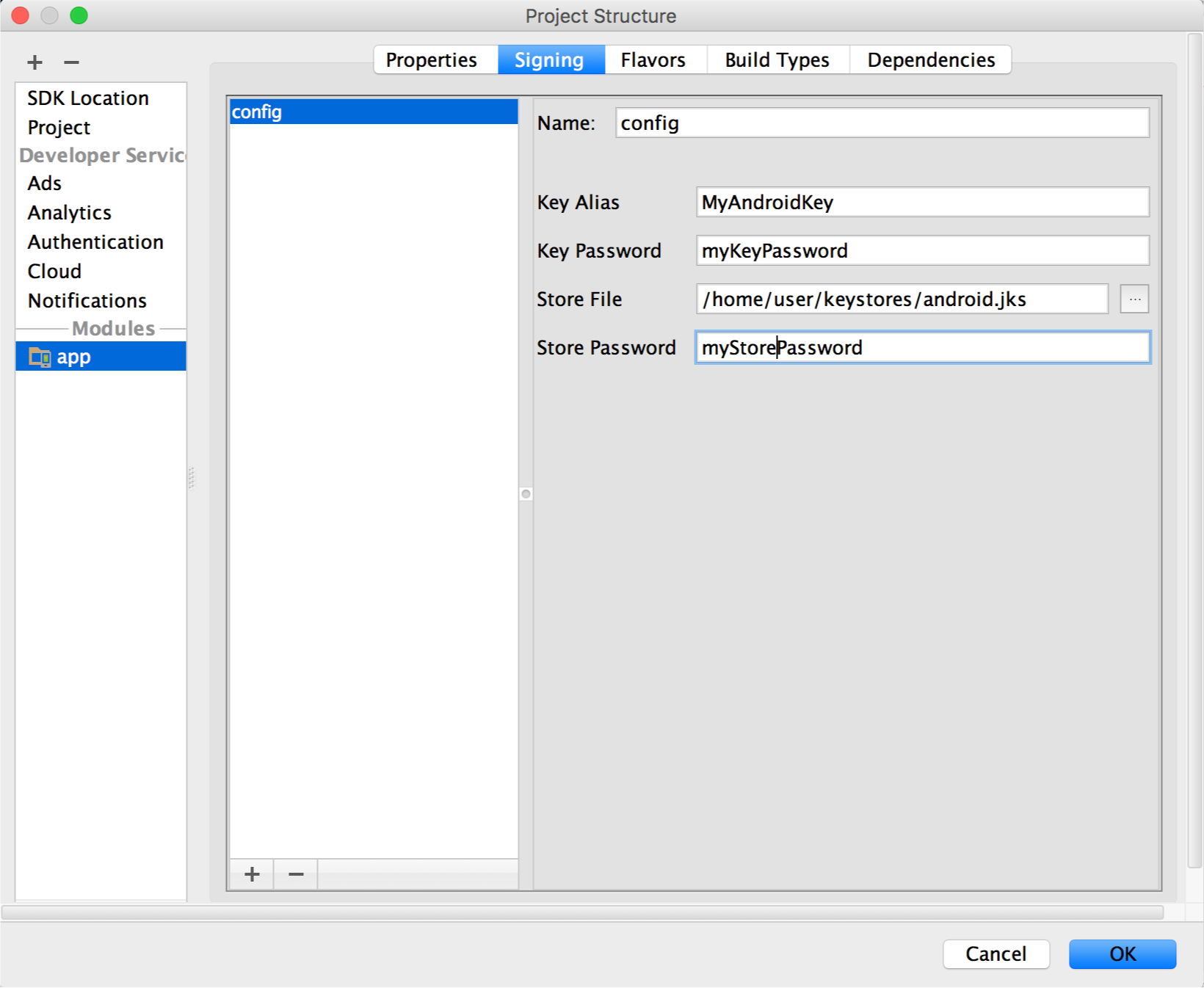
Figure 7. The window for creating a new signing configuration.
- Click the Build Types tab.
- Click the release build.
-
Under Signing Config, select the signing configuration you just created.
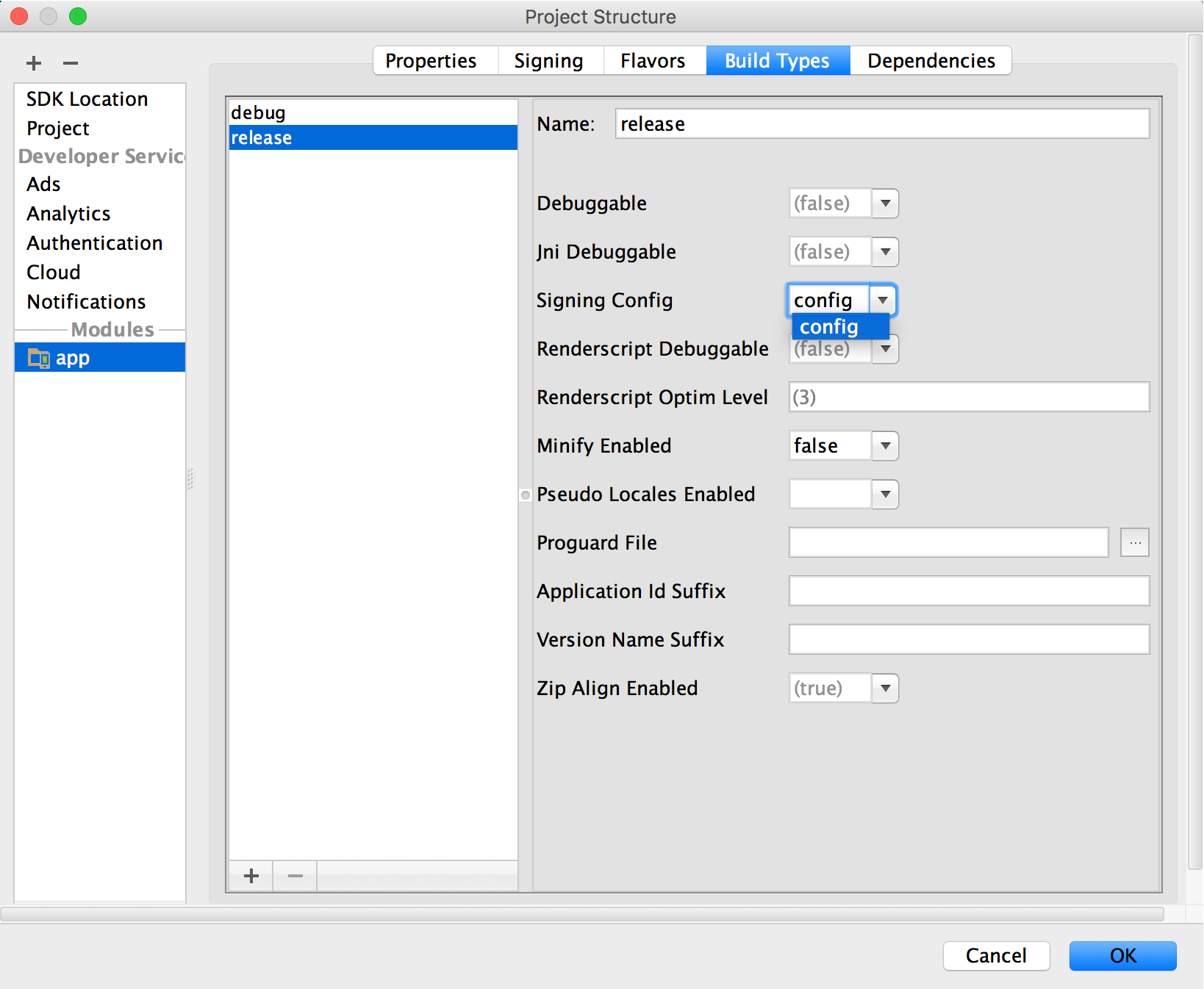
Figure 8. Select a signing configuration in Android Studio.
- Click OK.
Now every fourth dimension you lot build your release build blazon by selecting an pick under Build > Build Packet(s) / APK(south) in Android Studio, the IDE will sign your app automatically, using the signing configuration yous specified. You can detect your signed APK or app bundle in the build/outputs/ directory inside the project directory for the module yous are edifice.
When you create a signing configuration, your signing information is included in apparently text in your Gradle build files. If you lot are working in a squad or sharing your code publicly, you should proceed your signing information secure by removing it from the build files and storing it separately. You can read more than near how to remove your signing information from your build files in Remove Signing Information from Your Build Files. For more than about keeping your signing data secure, read Secure your primal.
Sign each production flavor differently
If your app uses product flavors and you would like to sign each flavor differently, you tin create additional signing configurations and assign them by flavor:
- In the Project window, correct click on your app and click Open up Module Settings.
- On the Project Structure window, under Modules in the left console, click the module you would like to sign.
- Click the Signing tab, so click Add
 .
. -
Select your keystore file, enter a name for this signing configuration (as you may create more than than one), and enter the required information.

Figure x. The window for creating a new signing configuration.
- Repeat steps three and 4 as necessary until you take created all your signing configurations.
- Click the Flavors tab.
- Click the flavor you would like to configure, so select the advisable signing configuration from the Signing Config dropdown menu.
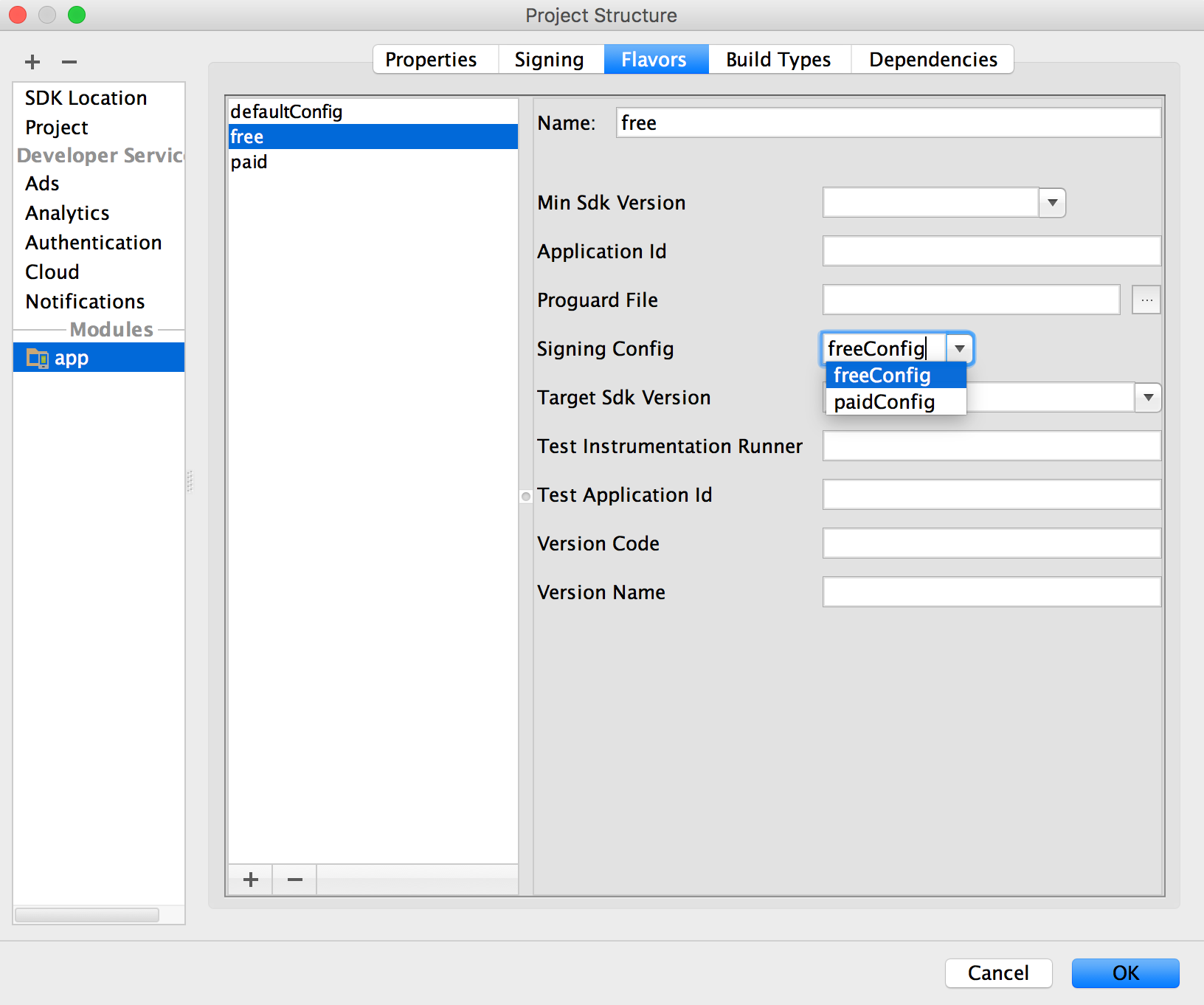
Figure 11. Configure signing settings past product flavor.
Echo to configure any additional product flavors.
- Click OK.
You tin also specify your signing settings in Gradle configuration files. For more than information, meet Configuring Signing Settings.
Manage your own signing key
If you choose not to opt in to Play App Signing (only for apps created earlier Baronial 2021), yous can manage your ain app signing key and keystore. Continue in mind, you lot are responsible for securing the key and the keystore. Additionally, your app volition non exist able to support Android App Bundles, Play Feature Delivery and Play Nugget Delivery.
When yous are ready to create your own key and keystore, brand sure you first choose a strong countersign for your keystore and a separate stiff countersign for each private cardinal stored in the keystore. You must keep your keystore in a safe and secure place. If yous lose access to your app signing key or your key is compromised, Google cannot recollect the app signing key for y'all, and you will not be able to release new versions of your app to users as updates to the original app. For more than information, see Secure your key, below.
If you manage your ain app signing central and keystore, when you sign your APK, you lot will sign it locally using your app signing central and upload the signed APK directly to the Google Play Shop for distribution equally shown in effigy ten.
Effigy 12. Signing an app when you lot manage your own app signing central
When yous utilize Play App Signing, Google keeps your signing key safe, and ensures your apps are correctly signed and able to receive updates throughout their lifespans. Still, if y'all decide to manage your app signing key yourself, there are a few considerations you should keep in mind.
Signing considerations
You should sign your app with the same certificate throughout its expected lifespan. There are several reasons why you should exercise so:
- App upgrade: When the system is installing an update to an app, it compares the document(s) in the new version with those in the existing version. The system allows the update if the certificates match. If y'all sign the new version with a different certificate, you must assign a dissimilar package name to the app—in this case, the user installs the new version as a completely new app.
- App modularity: Android allows APKs signed past the same document to run in the same process, if the apps so request, so that the arrangement treats them as a single app. In this manner you tin deploy your app in modules, and users can update each of the modules independently.
- Code/information sharing through permissions: Android provides signature-based permissions enforcement, and then that an app tin expose functionality to another app that is signed with a specified certificate. By signing multiple APKs with the same certificate and using signature-based permissions checks, your apps tin can share lawmaking and data in a secure manner.
If y'all plan to support upgrades for an app, ensure that your app signing key has a validity period that exceeds the expected lifespan of that app. A validity catamenia of 25 years or more is recommended. When your cardinal's validity period expires, users volition no longer be able to seamlessly upgrade to new versions of your app.
If you program to publish your apps on Google Play, the key you use to sign your app must accept a validity catamenia catastrophe later 22 October 2033. Google Play enforces this requirement to ensure that users can seamlessly upgrade apps when new versions are bachelor.
Keep your cardinal secure
If you cull to manage and secure your app signing key and keystore yourself (instead of opting in to Play App Signing), securing your app signing key is of critical importance, both to you and to the user. If you lot allow someone to use your fundamental, or if you leave your keystore and passwords in an unsecured location such that a third-party could find and use them, your authoring identity and the trust of the user are compromised.
If a tertiary party should manage to take your app signing cardinal without your noesis or permission, that person could sign and distribute apps that maliciously supervene upon your authentic apps or corrupt them. Such a person could also sign and distribute apps nether your identity that attack other apps or the organization itself, or decadent or steal user data.
Your private key is required for signing all hereafter versions of your app. If y'all lose or misplace your key, y'all volition not be able to publish updates to your existing app. You cannot regenerate a previously generated key.
Your reputation as a programmer entity depends on your securing your app signing key properly, at all times, until the primal is expired. Here are some tips for keeping your cardinal secure:
- Select strong passwords for the keystore and key.
- Do not give or lend anyone your private key, and do not let unauthorized persons know your keystore and key passwords.
- Go along the keystore file containing your private key in a safe, secure place.
In general, if you follow common-sense precautions when generating, using, and storing your key, it will remain secure.
Remove signing information from your build files
When you create a signing configuration, Android Studio adds your signing information in plainly text to the module's build.gradle files. If you are working with a squad or open-sourcing your code, y'all should move this sensitive information out of the build files so it is not hands accessible to others. To exercise this, you should create a separate properties file to shop secure data and refer to that file in your build files as follows:
- Create a signing configuration, and assign it to one or more build types. These instructions assume yous have configured a single signing configuration for your release build type, as described in Configure the build process to automatically sign your app, higher up.
- Create a file named
keystore.propertiesin the root directory of your project. This file should incorporate your signing information, every bit follows:storePassword=myStorePassword keyPassword=mykeyPassword keyAlias=myKeyAlias storeFile=myStoreFileLocation
- In your module'south
build.gradlefile, add code to load yourkeystore.propertiesfile before theandroid {}cake.Great
... // Create a variable chosen keystorePropertiesFile, and initialize information technology to your // keystore.properties file, in the rootProject binder. def keystorePropertiesFile = rootProject.file("keystore.properties") // Initialize a new Backdrop() object chosen keystoreProperties. def keystoreProperties = new Properties() // Load your keystore.properties file into the keystoreProperties object. keystoreProperties.load(new FileInputStream(keystorePropertiesFile)) android { ... }Kotlin
... import coffee.util.Properties import java.io.FileInputStream // Create a variable chosen keystorePropertiesFile, and initialize it to your // keystore.properties file, in the rootProject folder. val keystorePropertiesFile = rootProject.file("keystore.properties") // Initialize a new Properties() object called keystoreProperties. val keystoreProperties = Properties() // Load your keystore.backdrop file into the keystoreProperties object. keystoreProperties.load(FileInputStream(keystorePropertiesFile)) android { ... }Note: Yous could choose to shop your
keystore.backdropfile in another location (for case, in the module folder rather than the root binder for the project, or on your build server if you are using a continuous integration tool). In that case, you lot should change the code above to correctly initializekeystorePropertiesFileusing your actualkeystore.propertiesfile'southward location. - You lot can refer to properties stored in
keystorePropertiesusing the syntaxkeystoreProperties['propertyName']. Modify thesigningConfigsblock of your module'sbuild.gradlefile to reference the signing information stored inkeystorePropertiesusing this syntax.Great
android { signingConfigs { config { keyAlias keystoreProperties['keyAlias'] keyPassword keystoreProperties['keyPassword'] storeFile file(keystoreProperties['storeFile']) storePassword keystoreProperties['storePassword'] } } ... }Kotlin
android { signingConfigs { getByName("config") { keyAlias = keystoreProperties["keyAlias"] keyPassword = keystoreProperties["keyPassword"] storeFile = file(keystoreProperties["storeFile"]) storePassword = keystoreProperties["storePassword"] } } ... } - Open up the Build Variants tool window and ensure that the release build blazon is selected.
- Select an pick nether Build > Build Bundle(s) / APK(southward) to build either an APK or app bundle of your release build. You should come across the build output in the
build/outputs/directory for your module.
Because your build files no longer incorporate sensitive information, yous can now include them in source control or upload them to a shared codebase. Be sure to proceed the keystore.properties file secure. This may include removing it from your source command arrangement.
coppolawhichisatur.blogspot.com
Source: https://developer.android.com/studio/publish/app-signing
Post a Comment for "You Uploaded an Apk or Android App Bundle Signed With a Certificate That Expires Too Soon"